Welcome to my step-by-step guide on publishing your first-ever post using WordPress. Whether you’re looking to start a blog, run an e-commerce store, or simply share your ideas online, mastering WordPress content creation basics is essential. As a seasoned WordPress professional, I’ll show you everything from setting up your website to scheduling posts for search engine success. Let’s get cracking!
Getting Started with WordPress
Before we dive right into creating content, it’s essential to understand what WordPress is. In a nutshell, WordPress is a flexible content management system (CMS) that powers over 40% of all websites. The core platform is open-source, meaning anyone can use and modify it for free.
So, what sets WordPress apart from traditional website builders? Two key advantages:
- Customisation: WordPress offers thousands of themes and plugins to tailor the design and functionality. This allows you to create truly unique sites.
- Content Focus: With WordPress, your website dynamically displays content from a database. This content-first approach makes managing blogs, news sites, membership portals, and online stores easy.
Now that you grasp the basics let’s explore the two main ways average users interact with WordPress:
- As a hosted platform at WordPress.com
- As downloadable open-source software at WordPress.org
The WordPress.com route means they handle all the hosting and security for you. The tradeoff is less flexibility compared to the self-hosted open-source version. But fret not! I’ll cover both scenarios in this guide.
Accessing the WordPress Dashboard
To begin your WordPress journey, you need access to the administrative dashboard. Consider this your mission control for content creation and website management.
WordPress.com
If using the hosted WordPress.com platform, simply:
- Go to www.wordpress.com
- Click on “Log In”
- Enter your WordPress.com username and password
That’s it! The dashboard lets you create post pages and modify your site’s design and settings.
Self-Hosted WordPress.org
For the open-source WordPress.org software, you’ll need:
- A domain name (your website address)
- Web hosting configured for WordPress
Once you have a hosting setup, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your domain name
- Find and click the “wp-login” page link
- Enter the username and password for your WordPress admin account
This login grants you access to the all-powerful dashboard for managing your self-hosted WordPress site. Should you create a page or post?
Creating Your First Post
Now for the fun part – let’s publish your first post!
WordPress refers to posts as the chronological articles, stories, blog entries, and announcements that comprise the primary content. Posts typically show on your blog page or related category and tag archives.
Accessing the Post Editor
WordPress.com
- Click “My Site” and select “Blog Posts”
- Click the blue “Create a Post” (or “Create Blog Post”) button
WordPress Self-Hosted
- Hover over “Posts” in the left sidebar
- Click on “Add New.”
This will open the post editor – your one-stop shop for crafting remarkable blog posts.
Structuring Your Post
The key to writing compelling posts lies in proper structure and formatting. Here are my top tips for organising your content:
- Headline – Summarize the essence of your post in 55 characters or less
- Introduction – Explain the purpose and set reader expectations
- Body – Elaborate on your main ideas with research, examples, and anecdotes
- Conclusion – Recap key points and include a call to action if needed
- Images – Break up text with relevant photos, graphics and visual media
- Links – Provide references and links to external sources where applicable
Follow this basic structure using the block editor’s headings, paragraphs, lists, quotes, and more to make your content scannable and compelling.

Enhancing Your Post
WordPress offers built-in options to enhance your posts, including:
Featured Images
Also known as post thumbnails, featured images appear prominently on your blog page, social media shares, and Google search listings. For best results:
- Upload an eye-catching, relevant image
- Optimise it to load fast
- Choose landscape dimensions for flexibility
Categories
Categories help group related posts together. For example, you may have an “Ocean Conservation” category containing articles on sustainability. Use categories liberally to organise your site’s content.
Tags
Whereas Categories are broad topics, Tags add more granular details on specific subjects within a post. For instance, you could tag an article on coral bleaching with “Environment” and “Climate Change”. Tags aid content discovery.
Excerpts
Excerpts are short descriptions previewing your post content. Much like a movie trailer, well-written excerpts entice readers to click and view the full article.
By leveraging these enhancements strategically, you’ll amplify your post’s visibility and engagement.
Reviewing and Publishing Your Post
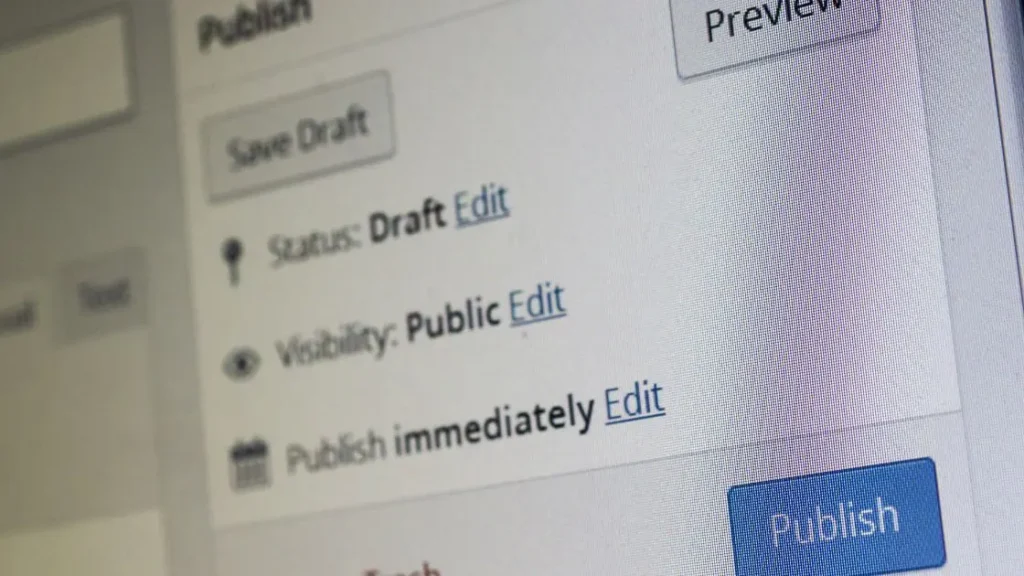
Before officially publishing, always review your post thoroughly using the preview button. This displays exactly how your content will appear once live. Spend time checking for typos, formatting issues, broken images or links.
When ready, click “Publish” for your post to go live immediately. Alternatively, you can schedule posts to publish automatically in the future – perfect for social media marketing campaigns.
Under the “Visibility” setting, you can also password-protect posts or privately share them with just your team. WordPress lets you control precisely who sees your content.
Finally, don’t forget to share your newly minted blog post on social media! Connect your accounts in the WordPress settings accordingly.
And voila! With that, you’ve successfully created your first bit of blog content. Pat yourself on the back – it only gets more accessible and more fun from here!
Critical Differences Between Posts and Pages
Now that you know how to create standard WordPress posts, let’s discuss the distinction between posts and pages.
Posts are blog or news entries organised chronologically by publish date. Posts focus on time-sensitive content.
Pages contain more evergreen, static information like “About” or “Contact” details. Pages prioritise structure over chronology.
While both contain blocks of editable content, pages and posts serve different purposes:
- Posts – Timely articles, stories and announcements
- Pages – Static content like landing pages and core site info
Specific settings differ between page and post content in WordPress, from navigational menus to URL formats.
To manage consistency across your site, customise the format and design separately for posts and pages under the WordPress Settings > Reading page.
Expanding Your WordPress Skills
Creating that initial post marks a significant milestone, but it’s the first step in mastering WordPress content creation.
Here are some recommended next steps:
- Experiment with multimedia – Embed video, audio, surveys and more to create multi-dimensional storytelling
- Explore plugins – Extend WordPress capabilities using plugins like contact forms, e-commerce and SEO
- Use reusable blocks – Design customizable content blocks to efficiently maintain site-wide standards
- Collaborate with teams – Invite contributors, editors and administrators to publish collaboratively
The more you use WordPress, the more adept you become. Stay curious, embrace creativity, and have fun showcasing your ideas online. If you want Meta Trends to create a fantastic custom website for your business, please get in touch.
So tell me – what will you publish next? Which topics excite you? I’d be thrilled to hear about your WordPress plans and answer any questions you have.
Let your blogging adventure begin! Write on, mate!
